20 Historical Events That Radically Changed the World
Originally published by Crispus in October 2022 and updated by Vanessa M in March 2024.
History is important in our everyday lives. It defines who we are as a people, and also helps in shaping the society we live in. The world we live in today entirely depends on historical events that have happened in the past.
Through extensive research, we have listed some of the most important historical events that drastically changed the world. Some happened centuries ago while some have happened during our lifetime, but they all have greatly changed our way of life and most importantly our way of understanding the world we live in.
1. Slave Trade – the 16th to the 19th Centuries
Described as the biggest human rights violations of all time; the Slave trade is one major event that changed the world permanently. The movement of millions of Africans to the New World, during a period of roughly four hundred years, was by any standard, a major historical phenomenon.
The long-term economic exploitation of millions of black slaves was to have a profound effect on the New World’s history. Most fundamentally, it produced deep social divides between the rich white and poor black communities, the consequences of which still haunt many societies today, many years after emancipation.
It also had devastating social and economic effects in Africa as warlords and tribal chiefs’ engagement in the slave trade promoted an atmosphere of lawlessness and violence.
2. The First World War – 1914 to 1918
Photo by Heiddy2 from Wikimedia
The First World War was a major global conflict that began on 28 July 1914 and ended on 11 November 1918. It involved more than 100 countries from Europe, the Americas, Asia, Australasia, and Africa.
The fighting took place across Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and parts of Asia, and it is one of the deadliest conflicts in history. An estimated 9 million soldiers died in combat, with another 5 million civilian deaths as a result of military actions, hunger, and disease.
The war also saw the introduction of most military technologies used today like machine guns, tanks, aerial combat, submarines, chemical weapons, and radio communications.
Politically, World War 1 contributed to the fall of four imperial dynasties, namely Germany, Austria-Hungary, Russia, and the Ottoman Empire. It also laid the grounds for the rise of new world order which later played a big role in the breakout of the Second World War.
3. Introduction of Electricity – The 19th Century
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, electricity was not part of the everyday life of many people, even in the industrialized Western world. First introduced into people’s homes in the late 19th century, electricity is arguably the greatest invention in human history.
The introduction of Electricity opened up a whole new world, and most of the inventions we see today would have never happened without it. Since its invention, electricity had changed every aspect of people’s lives. Communication, transportation, heating, cooling, food production, healthcare, manufacturing, national security, and the economy are all enabled by electricity.
Demand for electricity has continued to increase more and more as the world population grows. However, environmental concerns have led to an increased focus on generation from renewable sources in particular from wind and solar.
4. The Second World War – 1939 to 1945

Photo Source: Wikimedia
The Second World War (WWII) is one of the major transformative historical that fundamentally changed the world. It lasted from 1939 to 1945 and directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries.
The war marked the beginning of a technological revolution like digital communication, jet engines, the development of nuclear weapons, and the introduction of naval aircraft careers. Other technological and engineering feats achieved during, or as a result of, the war include the world’s first programmable computers guided missiles and modern rockets.
As a consequence of the war, the United Nations was created in order to harmonize international cooperation and diplomacy. It also marked the decline of all European colonial empires which resulted in the independence of African and Asian countries.
5. The Development of Atomic Bomb – 1945
The development and usage of the first atomic bombs have caused a change in the military, political, and public functionality of the world today. Its invention and usage in the 1940s drastically changed the global power equation, with the United States and the former USSR becoming the world military superpowers.
This changed world geopolitics forever and the rivalry between the two superpowers led to the Cold War, which in turn led to the nuclear arms race.
Despite the fall of the USSR in 1991, the nuclear arms race still persists with an estimated 13,410 nuclear warheads in the world today. Most of the nuclear warheads are possessed by the United States and Russia but the United Kingdom, France, China, India, Pakistan, Israel, and North Korea also possess a substantial number of nuclear warheads.
Although it is over 70 years now since a nuclear weapon was deployed in a war field, the threat of its possible deployment still remains.
6. The Black Death – the 14th Century
The 14th-century epidemic of the “Black Death,” also called the black plague or bubonic plague, across Europe and Asia, has become one of the most infamous events in history. The plague killed 30-60 percent of the entire population of Europe, claiming a grand total of anywhere between 75 to 200 million lives.
Due to its devastation, the world’s Population growth did not resume until a full century later and did not recover until the 17th century. Their effects on religious, social, and economic activities were permanent.
7. Attack on Pearl Harbour – 1941

Photo Source: Wikimedia
The attack on Pearl Harbour was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service on the United States naval base at Pearl Harbour in Honolulu. It happened just before 8:00 a.m., on Sunday, December 7, 1941.
The attack was a pivotal moment in world history which consequently marked the entry of the USA into the Second World War and set in motion a series of events that would transform the country into a global superpower and guardian of international order.
For years, Japan sought expansion in Asia and the Pacific, aiming to control the entire region and its rich resources. The attack on Pearl Harbour was meant to help achieve that goal, but it actually worked completely against the nation’s end game.
As a result of the attack, Japan was defeated and disarmed, its empire dissolved, its form of government changed to a democracy, and its economy and education system reorganized and rebuilt.
8. The reign of Adolf Hitler – 1933 to 1945

Photo by Kentot785 from Wikimedia
Adolf Hitler, the leader of Germany’s Nazi Party, was one of the most influential and notorious dictators of the 20th century. He capitalized on economic woes, popular discontent, and political infighting to take absolute power in Germany beginning in 1933.
His invasion of Poland in September 1939 drove Great Britain and France to declare war on Germany, marking the beginning of World War II which is by far the most costly war in terms of human life estimated to be 56 million.
Following Hitler’s rise to power in German, the regime built a network of concentration camps in Germany and other parts of Eastern Europe which were responsible for almost wiping out the Jewish communities in Europe.
9. The holocaust – 1940 to 1945
The Holocaust was the deliberate, systematic murder of millions of Jews and other minorities during World War II by Hitler’s Nazi regime in Europe. Many historians consider the Holocaust the worst event in history and have described Hitler, his followers, and his regime as evil.
During the holocaust, over six million Jews from all over Europe were transported and eventually killed in various concentrations. Other victims of the holocaust included Jehovah’s Witnesses, homosexuals, Gypsies, and other minority groups.
The Holocaust left millions of refugees, including many Jews who had lost most or all of their family members and possessions. It also had a deep effect on society both in Europe and the rest of the world, and today its consequences are still being felt.
10. Foundation of United Nations – 1945

Photo by Lateiner from Wikimedia
The United Nations was officially formed on 24 October 1945. Its main purpose is to prevent war and coordinate humanitarian efforts to reduce poverty, uphold international law, and protect the environment.
Although the UN has often failed to stop conflicts between member states, it is still an important international organization with a mandate to uphold basic universal rights and freedoms without distinction or discrimination.
It also established the first international Court of Justice at The Hague. The UN has played a role in global humanitarian efforts and UN bodies such as the Global smallpox eradication program.
Since its formation, the United Nations has largely been successful in maintaining peace and harmony among the member states, protecting the environment, and advocating for human rights.
11. Colonization – The 19th to the 20th Centuries
The historical effects of the colonial period stretch across centuries, and across all the continents of the world. From the 16th century onward, several European powers set up colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
On many continents, colonialism caused changes in culture, language, society, and economics; it also caused the deaths of millions as the colonizers brutalized the natives, mostly through private enterprises with the blessings of their governments. The colonial period officially ended in 1999, after Portugal transferred Macau to China.
12. The Formation of USSR – 1922

Naval Ensign of the Soviet Union – Photo by Zscout370 from Wikimedia
The Soviet Union was formed in 1922 and was one of the two world superpowers until its collapse in 1991. It was home to over 300 million people and occupied 1/6 of all Earth’s land.
The Soviet Union became one of the world’s largest and most powerful countries. It was ranked second in industrial production and had one of the biggest armies in the world.
Many former Soviet citizens have nostalgia for the USSR, pointing towards most infrastructures being built during the Soviet era, increased job security, increased literacy rate, as well as political stability.
13. Decolonization –The Mid and the Late 20th Century
Almost all of the major nations that were involved in World War II began shedding their overseas colonies soon after the conflict. Immediately after the war, European powers began a decades-long process of withdrawing from their possessions in Africa and Asia.
In 1946, there were 35 member states in the United Nations, but as the newly independent nations joined the organization, by 1970 membership had increased to 127 member states.
The emergence of newly independent countries in Africa and Asia that used the borders of the imperial partitions later led to further conflict. In many cases, these conflicts pitted historically antagonistic ethnic or religious groups which now needed to share the same country which was arbitrarily divided by European powers.
14. The Cold War – 1946 to 1991
During the Yalta Conference, the Western capitalist powers and the communist Soviet Union agreed to set separate spheres of influence in Europe, they set up the stage for a geopolitical rivalry that dominated the world for the next five decades.
The two rival blocks formed mutual defense organizations, with the west forming the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) in 1949 and the East forming the Warsaw Pact in 1955. Each block was determined to expand its own influence among neutral countries and limit the influence of its rivals.
With Cold War tensions running high, the two blocks took their rivalry to space, with the Soviet launch of Sputnik in 1957, and the United States astronauts landing on the Moon on 20 July 1969.
15. Discovery of HIV AIDS – 1981
There are very few things that have drastically changed the world more than HIV AIDS. Since its discovery among young gay men in New York and San Francisco in 1981, HIV AIDS has become one of the most devastating pandemics in human history.
The epidemic has caused untold human suffering, social disintegration, and economic destruction. It has also left millions of children orphaned, has disrupted village and community life, and has increasingly affected the development and economic growth of nations.
Overall, HIV AIDS has impacted the global public health system with an estimated 40 million people living with HIV AIDS in the world today. It has also challenged some of the communities’ traditional practices as well as influenced a drastic human behavior change.
16. The fall of Berlin Wall – 1989

Berlin Wall Potsdamer Platz November 1975 – Photo by Edward Valachovic from Wikimedia
The fall of the Berlin Wall on 9 November 1989, was a pivotal event in world history that marked the falling of the Iron Curtain and one of the series of events that started the fall of communism in Eastern and Central Europe.
It was a guarded concrete barrier that divided Berlin from 1961 to 1989, and encircled West Berlin, separating it from East German territory. It symbolized the true dividing line between democracy and communism during the Cold War.
After the fall of the Berlin Wall, it became clear that the Soviet Union’s control of Eastern Europe could not continue and it led to the breaking up of the Warsaw Pact and eventually the reunification of Germany.
17. The Dissolution of the Soviet Union – 1991
The dissolution of the Soviet Union was the process of internal disintegration within the Soviet Union (USSR) which resulted in the end of the country’s and its federal government’s existence as a sovereign state, thereby resulting in its constituent republics gaining full sovereignty on 26 December 1991.
Its collapse caught many people by surprise., and the economic breakdown that followed led to a severe economic crisis and catastrophic fall in the standard of living in post-Soviet states and the former Eastern Bloc, which was even worse than the Great Depression.
The collapse of the Soviet Union marked the end of the cold war and most of the former Warsaw Pact states became part of the European Union and joined NATO, while some of the other former Soviet republics have been publicly expressing interest in following the same path.
18. Invention of Internet – 1989
In the world, today Internet has come to be among the main mediums of communication. It’s come to be the lifeline of survival. It’s eliminated the whole social, economic, and physiological obstacles and has an immense impact on people’s daily lives.
The Internet was invented in 1989 by Tim Berners-Lee, and it changed the way we communicate, the way we store information, and the way we interact as human beings.
19. The World Trade Centre Terrorist Attack – 2001

Photo by Robert J. Fisch from Wikimedia
The world trade center terrorist attack of September 11, 2001, was the biggest single terrorist attack in the history of the United States. The sheer magnitude of the attack, destruction, and scale of death shocked the US and the entire world.
The event changed most countries’ foreign policies and reshaped the global response to terrorism. It also raised new and troubling questions about the security, privacy, and treatment of various groups of people perceived to be supporting terrorism.
The global response to the 9/11 attack, namely the invasion of Afghanistan and Iraq, has deeply destabilized the Middle East and North Africa region. This has caused the emergence of new radical terrorist groups, which continue to threaten the core existence of humankind.
20. The Outbreak of Covid19 – 2019
The novel human coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was first reported in Wuhan, China, in 2019, and subsequently spread globally to become the world’s deadliest pandemic since the 1918 Spanish flu pandemic.
The consequences of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak are unprecedented and felt around the world. Every aspect of people’s lives across the globe has profoundly been affected. In addition to the threat to public health, the economic and social disruption threatens the long-term livelihoods and well-being of millions.
Over the past three years of COVID-19, the world has seen a drastic change in people’s behaviors including how people live, travel, communicate, and relate.
Life after the Events: 20 Untold Stories from History’s Aftershocks
1. Legacy of the Slave Trade

John Raphael Smith; S. Morgan; after George Morland, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Following the abolition of the slave trade in the nineteenth century, echoes of emancipation reverberated throughout communities burdened by centuries of oppression. Untold stories of resilience emerged as former slaves embarked on a moving journey of rebuilding lives and forging new identities.
Individuals freed from the shackles of the past contributed to the vibrant tapestry of cultures in the Americas. These untold stories reveal the strength and determination of a people determined to rise above the shadows of enslavement, leaving an indelible mark on the changing history of a post-abolition world.
2. Post-World War I Realities
In the aftermath of World War I, a generation traumatized by the horrors of war sought solace and renewal. Untold stories of camaraderie emerged as war veterans, united by their shared trauma, formed profound bonds that crossed borders.
These connections fueled movements advocating for peace and international cooperation, as the scars of war bred a collective desire for a world free of conflict. The echoes of trenches, while bearing the weight of a devastating past, also bore witness to the resilient spirit of those who, through unity, aimed to build a more harmonious and interconnected global community.
3. Illuminating lives

Photo by Daniel Reche from Pexels
Electricity was introduced in the nineteenth century, illuminating a dark world and sparking untold stories of transformation. Communities embraced this technological marvel, resulting in a slew of opportunities for education, innovation, and connectivity. As light bulbs came to life, so did the minds of those who had previously been confined to dimly lit spaces.
This electrifying change paved the way for advancements that would span generations, propelling societies into an era of unprecedented progress. Untold stories emerged as the glow of electricity not only brightened physical spaces but also rekindled the flame of human potential, illuminating lives with new possibilities.
4. Rebuilding Nations
Following World War II, devastated nations rose from the ashes, creating a symphony of resilience. Untold stories of reconstruction emerged as communities, undeterred by the devastation of war, banded together to rebuild. The spirit of collaboration crossed borders, revitalizing shattered infrastructures, economies, and lives.
Amidst the rubble, stories of determination emerged, demonstrating the triumph of the human spirit over adversity. These untold stories reveal the collective strength that propelled nations forward, transforming the scars of war into the foundations for a brighter, more interconnected world. They planted seeds of hope during the rebuilding process, and they are still blooming today.
5. The Atomic Shadows

Charles Levy, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Following the development of the atomic bomb, a haunting shadow fell over global geopolitics. Untold stories emerged as nations confronted the ominous implications of nuclear weapons. Amid the uncertainty, movements advocating for disarmament and peace emerged, challenging the status quo.
Individuals from all over the world, haunted by the threat of mutually assured destruction, have banded together to seek a world free of nuclear weapons. These untold stories reflect the collective desire for a safer and more harmonious world, one in which the atomic shadows fade and humanity stands united against the looming threat of cataclysmic war.
6. Black Death’s aftermath
Following the Black Death, survivors faced the daunting task of rebuilding societies shattered by the relentless pandemic. Communities embarked on a transformative journey, revealing previously untold stories of resilience and renewal. In the aftermath of unprecedented loss, cultural norms were redefined, religious practices were reshaped, and economic foundations were restructured.
In the aftermath of the devastation, communities found the strength to adapt, fostering a collective determination to create a new normal. These untold stories reveal the indomitable spirit that rose from the depths of despair, laying the groundwork for a new societal fabric shaped by endurance and adaptation.
7. Pearl Harbour’s Impact

National Archives and Records Administration, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The attack on Pearl Harbor created seismic ripples that reshaped global power dynamics. Untold stories emerged as nations grappled with the profound implications, paving the way for transformative alliances and geopolitical shifts. In the aftermath, the United States emerged as the dominant global superpower, establishing the postwar order.
The aftermath of Pearl Harbor not only marked a watershed moment in World War II but also had an indelible impact on the course of global relations. These untold stories depict the intricate dance of diplomacy and power that unfolded in the aftermath of unprecedented conflict, shaping the contours of a new global order.
8. Hitler’s Legacy
Following Adolf Hitler’s reign, the world faced the haunting legacy of war and the atrocities of the Holocaust. Untold stories emerged as survivors, resilient in the face of unimaginable horrors, embarked on a journey to rebuild their shattered lives.
These narratives instilled a steadfast determination to never forget, laying the groundwork for global movements promoting tolerance and human rights. From the shadows of hatred and destruction emerged a collective determination to ensure that history’s lessons are passed down through generations, inspiring a world in which empathy and justice triumph over the darkness of the past.
9. Echoes of Holocaust
After the Holocaust, survivors faced the monumental task of rebuilding lives shattered by unspeakable horrors. Untold stories emerged as resilient communities came together in a heartfelt response to collective trauma. Memorials, educational initiatives, and resilient networks demonstrated an unwavering commitment to ensuring the world never forgets the atrocities of the past.
These untold stories became the foundation of a global movement, forging a collective memory that spans generations, instilling empathy, and serving as a solemn pledge to prevent history from repeating its darkest chapters. In the echoes of the Holocaust, communities found the strength to build a future based on remembrance and resilience.
10. Formation of the United Nations
The establishment of the United Nations (UN) signaled a new era of global cooperation. Untold stories highlight nations’ collaborative efforts to prevent conflicts, champion human rights, and address common global challenges. The ravages of war resulted in a collective commitment to promote peace and mutual understanding.
The United Nations became the focal point of diplomatic efforts, laying the groundwork for an interconnected world in which dialogue and cooperation triumphed over conflict. These untold stories reflect humanity’s evolving aspirations for a harmonious global order, crossing borders and forming alliances in pursuit of a shared destiny based on unity and cooperation.
11. Colonies Unbound
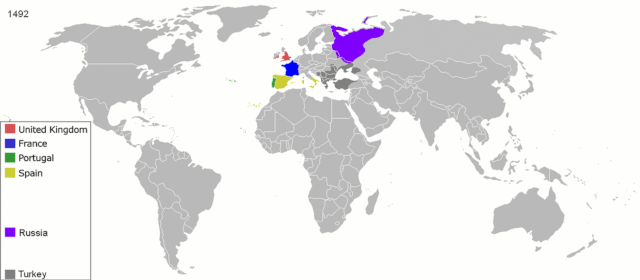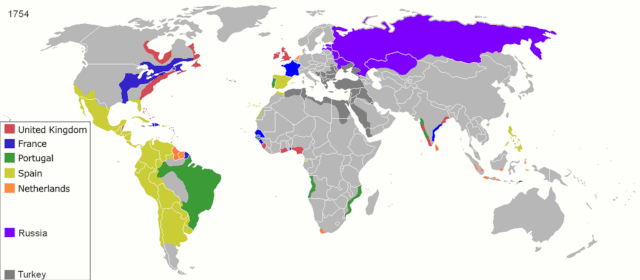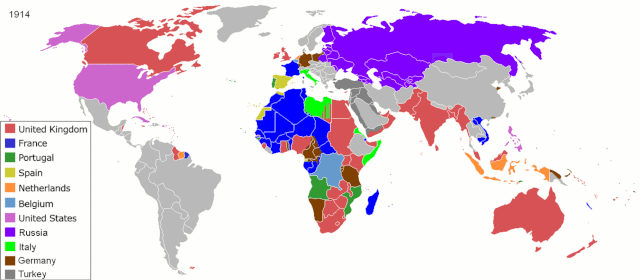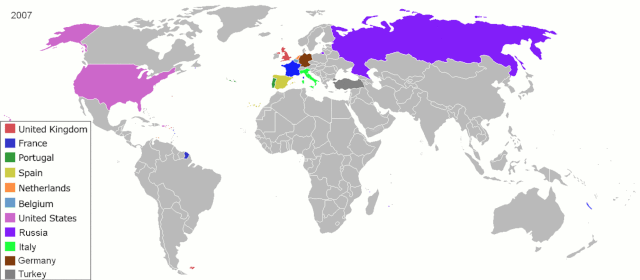
ArdadN at English Wikipedia, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The centuries-long aftermath of colonization reveals previously untold stories of cultural resilience and profound struggles for independence. Communities scarred by imperial rule forge paths of self-determination, reclaiming identities that had been suppressed during colonization. Resistance and resilience narratives emerge, depicting the arduous journey to nationhood and sovereignty.
Untold stories reflect the complex process of rebuilding nations while navigating postcolonial legacies. From linguistic revitalization to cultural reclamation, the stories reflect a moving legacy of triumph over oppression, recognizing the ongoing journey toward healing, identity restoration, and the establishment of just, independent societies in the face of historical injustices.
12. Birth and Dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union caused a seismic shift in geopolitics. As former Soviet states struggled with their newfound independence, untold stories emerged, creating a complex tapestry of political, economic, and cultural transitions. Amidst the echoes of the fallen empire, various narratives emerged, ranging from the difficulties of establishing new political identities to the economic restructuring that shaped post-Soviet landscapes.
These untold stories demonstrate the resilience of nations navigating uncharted waters and forging unique paths to sovereignty. The dissolution of the Soviet Union provided a canvas for a variety of stories, reflecting the complex dance of transformation and adaptation in the post-Cold War era.
13. Digital Dawn

BWenk, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The invention of the internet triggered a digital dawn, transforming communication and inspiring untold stories of adaptation. Individuals navigated a connected world, transforming industries and fostering a global dialogue that cut across geographical boundaries. As the digital realm challenged traditional power structures, untold stories emerged, ranging from grassroots movements to the redefinition of information dissemination.
The internet became a platform for innovation, amplifying voices, and democratizing information. These stories depict a paradigm shift in which individuals, aided by connectivity, reshaped the landscape of communication, ushering in an era in which the exchange of ideas and pursuit of knowledge transcended the constraints of physical space.
14. The Cold War’s Global Impact
The end of the Cold War heralded a transformative post-Cold War landscape. Untold stories emerged as countries navigated the complexities of shifting alliances, strengthening diplomatic ties, and adjusting to a world free of East-West rivalry. In the aftermath, former adversaries sought common ground, forming new bonds that transcended historical animosity.
The geopolitical chessboard was profoundly reconfigured, with nations seeking opportunities for cooperation rather than confrontation. These narratives capture nations’ resilience and adaptability as they collectively embraced the possibilities of a world free of Cold War tensions, ushering in a new era of collaboration.
15. Discovery of HIV/AIDS

https://pixabay.com/illustrations/ribbon-female-oncology-1524542/
The discovery of HIV/AIDS in the early 1980s revealed a tapestry of previously untold stories. Activism increased as communities banded together to combat stigma and raise awareness. Amid a devastating pandemic, medical breakthroughs emerged, shifting the narrative from despair to hope. Untold stories demonstrate the resilience of those affected, who form networks of support and care.
Communities came together in the face of adversity, overcoming societal barriers. Despite the challenges, untold stories highlight the tenacity of the human spirit, propelling advances in research, medical care, and compassion as the world grapples with the profound impact of the HIV/AIDS pandemic.
16. Fall of the Berlin Wall
The fall of the Berlin Wall broke down physical and ideological barriers, revealing untold stories of unity. Communities on both sides navigated the dismantling of barriers, fostering connections that transcended the concrete structure. The reunification of a divided Germany demonstrated resilience and collective aspirations.
Amid the crumbling concrete, stories of reconciliation and shared identity emerged. These untold stories depict a transformative moment when previously separated people came together in pursuit of a common future. The fall of walls not only reshaped the map but also left an imprint of unity overcoming the scars of division.
17. Dissolution of the Soviet Union

Zscout370, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 revealed a tapestry of untold stories. Economic challenges reverberated across post-Soviet states, resulting in severe crises and restructuring. Political transformations marked the transition from a superpower to independent nations dealing with newfound autonomy.
Untold stories highlight the struggles and triumphs of these emerging nations, each developing its own identity. Amid the dismantling of a massive geopolitical entity, the stories reflect the resilience of individuals navigating a rapidly changing landscape, capturing the complexities and aspirations of a region undergoing profound transformation and self-discovery.
18. Invention of the Internet
Untold stories of connectivity and transformation have emerged since the internet’s invention in 1989. Individuals worldwide adapted to a new era of information sharing, sparking a revolution in societal communication and interaction. These stories depict a world in which virtual realities overcame physical barriers, fostering an interconnected global community.
As the internet became an omnipresent force in daily life, untold stories emerged, from information democratization to the rise of online communities. The virtual realm evolved into a dynamic space where innovation flourished, mirroring the internet’s transformative power in weaving a narrative that connects people from all over the world.
19. World Trade Center Terrorist Attack
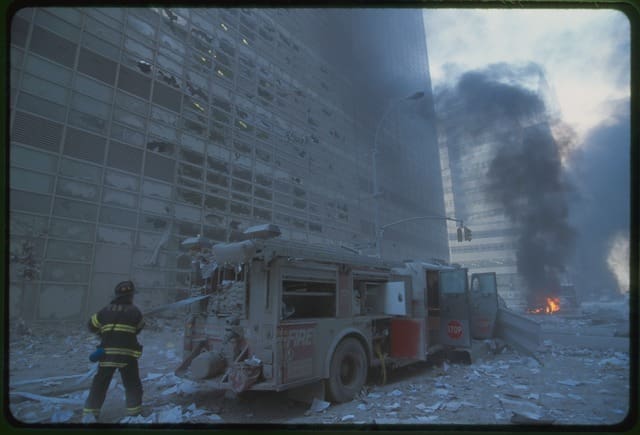

See page for author, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The aftermath of the 9/11 terrorist attack in 2001 reshaped global attitudes toward terrorism. Untold stories emerge in narratives of resilience, in which communities and nations demonstrate strength in the face of tragedy. International cooperation efforts emerged in response to the common threat, fostering anti-terrorist alliances.
These stories also reflect the pursuit of justice, as individuals and nations sought accountability for heinous crimes. The 9/11 attack’s lasting impact is rooted not only in the profound tragedy, but also in the untold stories of human endurance, collaborative responses, and the unwavering pursuit of a world free of the shadows of terrorism.
20. Impact of COVID-19
The COVID-19 outbreak spawned untold stories of adaptability and resilience. Global communities faced unprecedented challenges, sparking innovation and reshaping social norms. Throughout the crisis, stories of unity and interconnectedness emerged, demonstrating humanity’s collective response to a global health emergency.
From rapid vaccine development to digital transformations, untold stories demonstrated the indomitable spirit of individuals and communities. The pandemic sparked societal introspection, paving the way for new normalcy. In the face of adversity, these stories highlight humanity’s remarkable ability to adapt, collaborate, and forge ahead, emphasizing the common experiences that unite us all.
Untold stories from history reflect the human spirit’s resilience and adaptability. From the abolition of slavery to the digital age and the aftermath of the pandemic, these stories highlight the resilience of communities facing profound change. They discuss unity, innovation, and a common journey toward a more interconnected world. Every chapter highlights humanity’s ability to overcome obstacles and shape its future, leaving an indelible mark on the canvas of time.
Planning a trip to Paris ? Get ready !
These are Amazon’s best-selling travel products that you may need for coming to Paris.
Bookstore
- The best travel book : Rick Steves – Paris 2023 – Learn more here
- Fodor’s Paris 2024 – Learn more here
Travel Gear
- Venture Pal Lightweight Backpack – Learn more here
- Samsonite Winfield 2 28″ Luggage – Learn more here
- Swig Savvy’s Stainless Steel Insulated Water Bottle – Learn more here
Check Amazon’s best-seller list for the most popular travel accessories. We sometimes read this list just to find out what new travel products people are buying.










