Diagram showing ruminant’s digestive tract-by Davidbena-Wikimedia Commons
20 Interesting Facts About The Digestive System
Animal species have diverse digestive systems, which are categorized into four groups; monogastric, avian, ruminant, and pseudo-ruminant. The monogastric digestive system involves one single-compartmented stomach in which digestion happens. Animals with a monogastric system include humans, pigs, horses, dogs, rabbits, and cats. Only birds have the avian digestive system, which is highly unique compared to other digestive systems. Ruminants have a four-chambered stomach divided into the rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum. Examples of ruminants include cattle, sheep, goats, deer, and antelope.
Pseudo-ruminants are similar to ruminants the only difference is that they have a three-chambered stomach or a simple monogastric stomach. Examples of pseudo-ruminants include horses, hamsters, guinea pigs, and rabbits. The digestive system is in charge of processing food from the moment food enters the mouth until it is expelled. The system plays a crucial role in the body. It enables systems to process food, draw out the nutrients required from it, and get rid of waste. Here are some interesting facts about the digestive system.
Read also; 20 Weird Facts About The Human Body
1. The digestion of food involves numerous organs
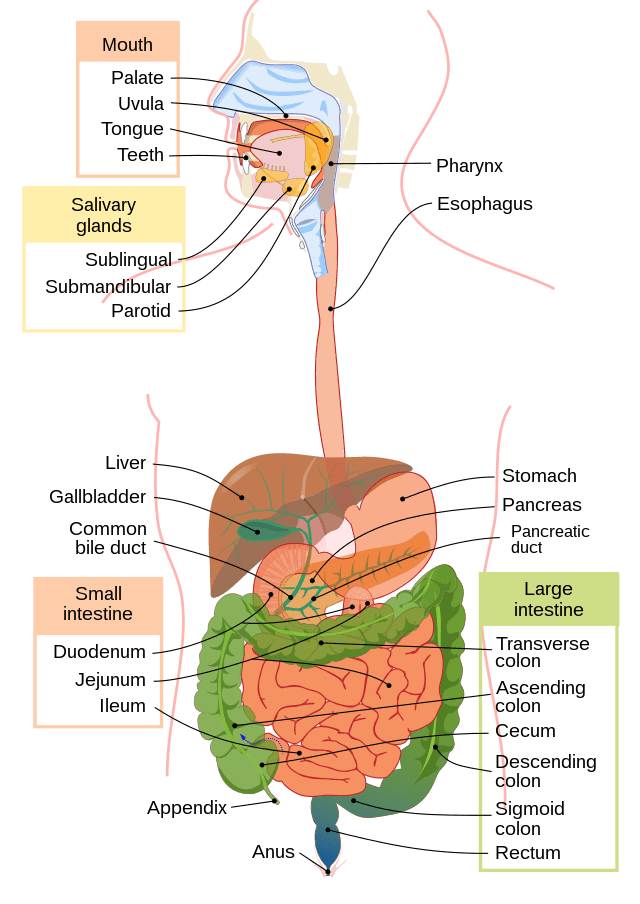
Gastrointestinal system-by USA Department of Health and Human Services-Wikimedia Commons
The digestive tract consists of the oral cavity and its related organs (lips, teeth, tongue, and salivary glands), the esophagus, the stomach in all species, the small intestine, the liver, the large intestine, and the rectum and anus. In humans, the enteric nervous system (ENS), the “second brain” which is made up of a large number of nerve cells regulates the function of the digestive system. For instance, when people get anxious the gut flips demonstrating the intimate relationship between the brain and the digestive system. While digesting is vital for life, fending against dangers is also crucial.
3. There are more than 100 million neurons in the human ENS

Neuron with ALL channels-by Dana Scarinci Zabaleta-Wikimedia Commons
The ENS has about 100 million neurons, which is one-thousandth of the brain and roughly one-tenth of the spinal cord’s total amount of neurons. The lining of the digestive tract contains the enteric nervous system.
4. Species differ tremendously in their digestive systems
To accommodate their dietary requirements, several digestive systems have evolved in various animal species. Monogastric digestive systems with a single-chambered stomach are seen in humans and many other animals. The digestive system of birds has developed to include a gizzard where food is broken down into smaller pieces. This makes up for their lack of mastication. Mostly plant-eating ruminants have a four-chambered stomach that breaks down roughage. While pseudo-ruminants lack the four-compartment stomach, they have similar digestive systems to ruminants.
5. The digestive system’s most crucial organ is the small intestine

Small-Intestine-highlighted-by US gov-Wikimedia Commons
The small intestine which consists of three parts the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum is the most crucial component of the digestive system and operates in both the digestion and absorption of food. The small intestine receives two digestive juices from the duodenum; bile and pancreatic juice which finishes the digestion of starch, proteins, carbs, etc. Another important role is that it absorbs simple molecules like glucose and amino acids after food has been broken down.
6. Food is broken down by enzymes in the digestive system
The orderly process of digestion of the main food macronutrients involves the activity of several digestive enzymes in both human and animals. Digestive enzymes from the stomach, salivary, and lingual glands break down proteins, while exocrine pancreatic gland enzymes break down carbs, proteins, lipids, RNA, and DNA. The luminal membranes and cytoplasm of the cells that line the small intestine contain additional digestive-process-aiding enzymes. The hydrochloric acid (HCl), which is released by the stomach, and the bile from the liver also help the enzymes work more effectively.
7. Food digestion necessitates collaboration between the digestive system and several other organ systems
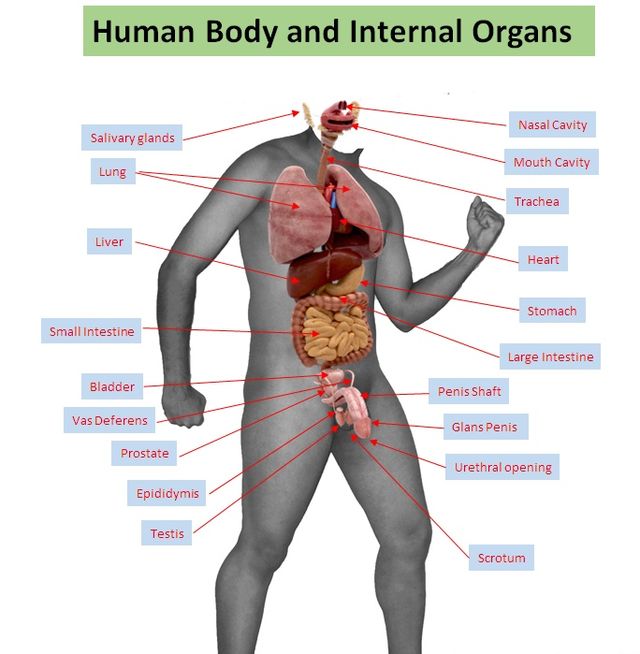
Human Body and Internal Organs (Labelled)-by Baresh25-Wikimedia Commons
Food digestion necessitates teamwork between the digestive system and various other organ systems, such as the neurological, cardiovascular, and muscular systems. For nutrients to be distributed in the body the digestive system works closely with the circulatory system which also aids in the speed of digestion. When food is ingested, the digestive organs require extra blood to accomplish their digestive duties. When food enters the digestive system, nerve impulses are delivered to the brain; in reaction, the brain sends information to the cardiovascular system, which causes the heart rate to increase and blood vessels in the digestive organs to widen. Food is moved along the digestive tract by rhythmic contractions of smooth muscles in the organ walls, hence the muscular system is also required for digestion.
8. Fiber plays a major role in digestive health
Fiber is the fuel that the colon cells use to be healthy. Dietary fiber, which is abundant in vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains, aids with regular bowel movements by keeping them smooth and regular. Although fibre can’t be broken by animal digestive enzymes, it absorbs extra water in diarrheic stools helping improve the digestive function. People who consume a high-fiber diet have significantly lower rates of constipation than those who follow a low-fiber diet, as well as fewer hemorrhoids and diverticula (outpouchings) in the colon. However, excess fiber can cause loose stools, bloating, and even diarrhea.
Read also; 15 Healthy Foods that are High in Potassium
9. A stomach can expand to hold around one quart of food
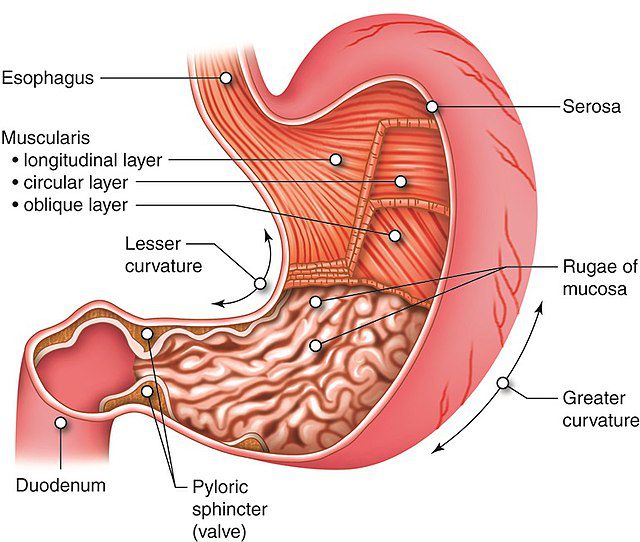
Anatomytool Muscles of the stomach – English-by Cenveo-Wikimedia Commons
A stomach can change in size and form based on the posture of your body and the amount of food within. An empty stomach measures roughly 12 inches in length and six inches broad at its widest point. A stomach can hold roughly 2.5 ounces of food when it is empty and relaxed in an adult. When expanded, it can accommodate around 1 quart of food. The rumen is the largest stomach compartment in cows and consists of many sacs that can hold up to 25 gallons of material depending on the cow’s size.
10. Food doesn’t need gravity to reach the stomach
Peristalsis, which occurs while eating, is a wave-like contraction and relaxation of the esophageal muscles that drive food into the stomach along the small canal. This process is not at all gravity-dependent. Because of this, astronauts do not have to be concerned about eating while floating in space. This explains why it is possible for us to eat while hanging upside down.
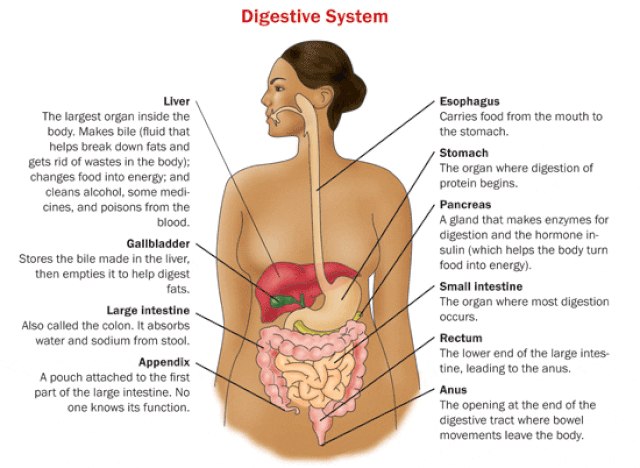
11. The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder play crucial roles in the digestive system
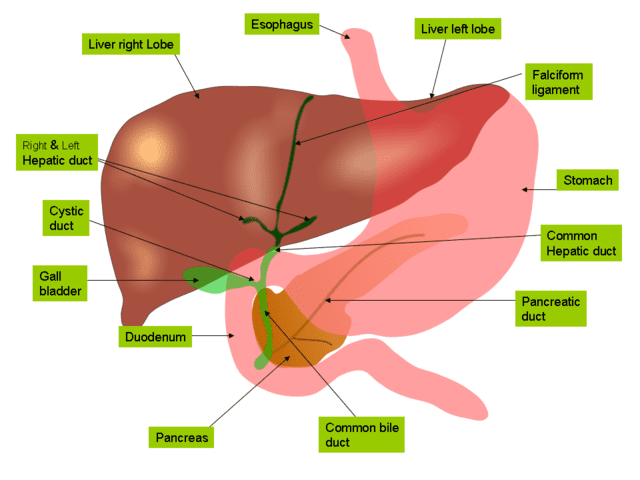
Anatomy of liver and gall bladder-by Jiju Kurian Punnoose-Wikimedia Commons
The liver and pancreas create fluids that the chyme encounters when it enters the small intestine. The pancreas secretes enzymes into the small intestine that break down protein, carbs, and fats, while the liver generates bile that is stored in the gallbladder and subsequently released into the small intestine to break down fats. Moreover, the pancreas secretes a chemical called bicarbonate, which neutralizes any stomach acid that escapes.
12. Food travels from the esophagus to the stomach in a period of 2 to 3 seconds
Food doesn’t merely fall into your stomach once it has passed through the esophagus and into your mouth. Instead, the food is slowly forced through the esophagus by wavy movements of the muscles that line its walls which takes two or three seconds.
13. The digestive process starts in the mouth

A person eating sushi by Ivan Samkov-Pexels
In most animals, the upper gastrointestinal system starts with the mouth, which has various structures that start the earliest stages of digestion. They include the tongue, teeth, and salivary glands. Saliva is a digestive juice produced by the salivary glands that helps food pass more readily past the esophagus and into the stomach. Moreover, saliva contains an enzyme that starts to break down dietary starches. The avian digestive system is different though because birds do not have teeth for chewing instead their digestion starts in the proventriculus which is the first part of the bird’s two-chambered stomach.
14. Each part of the digestive system is susceptible to a variety of illnesses
Each portion of the digestive system is vulnerable to a variety of illnesses, many of which are congenital. Mouth diseases can be caused by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, fungi, and as a side effect of some drugs. Tongue illnesses and salivary gland diseases are examples of mouth diseases such as; gingivitis, gingivostomatitis, and candidiasis. There are esophageal illnesses, such as the formation of Schatzki rings, which can narrow the esophagus and make swallowing difficult. They are also capable of entirely blocking the esophagus.
Stomach illnesses, such as gastroparesis, gastritis, and peptic ulcers, are frequently chronic conditions. A volvulus, which is an intestinal loop that twists and encloses the mesentery to which it is linked, can also clog the small intestine. In extreme cases, this may result in mesenteric ischemia. Diverticulitis is a frequent intestinal condition. Diverticula are tiny pouches that can develop inside the intestinal wall and can cause diverticulitis when they become inflamed. If an inflammatory diverticulum ruptures and an infection takes hold, this condition may develop problems.
15. Acidic foods can have an impact on the digestive tract

Citrus fruits by Jane Doan-Pexels
Citrus fruits including lemons, limes, oranges, and grapefruit, as well as tomato sauce, are acidic and can irritate the stomach lining, leading to digestive issues. Many individuals are unaware that carbonated beverages also contain acid. Avoid eating anything acidic if your stomach is irritated. Animals exposed to acids often experience symptoms within 90 minutes, which can linger for up to 12 hours. Disorientation, mydriasis, drowsiness, behavioral modifications (such as increased grooming and play), and even hallucinations are possible.
16. The human body’s digestion differs based on the diet
It takes roughly 6-8 hours for food to move through your stomach and small intestine after you eat. A meal with a high-fat content takes roughly 6 hours to digest, but a meal with a high carbohydrate content takes only 2 hours to digest. The more protein or fat there is in the diet, the longer it takes to digest. Basic carbohydrates, such as plain rice, pasta, or simple sugars, take 30 to 60 minutes to digest. It is necessary to ensure the intake of a balanced diet to ensure a healthy lifestyle and weight and prevent digestive difficulties.
Read also; Top 15 Nutrition Facts You Should Know About
17. Various hormones play vital roles in digestion

1802 Examples of Amine Peptide Protein and Steroid Hormone Structure-by OpenStax College-Wikimedia Commons
Hormones regulate the many digestive enzymes released in the stomach and intestine during digestion and absorption. In response to meal consumption, the hormone gastrin, for example, induces stomach acid output. The hormone somatostatin inhibits the production of stomach acid. Hormone secretin’s main physiological activities include pancreatic fluid stimulation and bicarbonate secretion.
18. The digestive system is important for immunological health
70% of immune cells are located in the gut. The lining of the digestive tract, which contains immune cells, aids in the filtering of nutrients and the prevention of poisons from entering the bloodstream. Taking vitamins, eating a well-balanced diet, exercising, and drinking plenty of water can all contribute to a strong immune and digestive system.
19. The liver is the largest organ in the digestive system

3D Medical Animation liver parts-by Scientific Animations-Wikimedia Commons
The liver is an auxiliary digestive gland that contributes to the body’s metabolism. It is the second-largest organ in the body (after the skin). The liver serves a variety of purposes, some of which are crucial for digestion. The liver can synthesize proteins, detoxify a variety of metabolites, and create the biochemicals required for digestion. It controls how much glycogen is stored and can produce glycogen from glucose (glycogenesis). Certain amino acids can be converted into glucose in the liver. The digestion of carbohydrates is a major part of its digestive processes. Moreover, it keeps the synthesis and breakdown of proteins under control.
20. An essential component of the body’s digestive system is the diaphragm
The body’s digestive system relies heavily on the diaphragm. The thoracic cavity, which houses the majority of the digestive organs, is divided from the abdominal cavity by the muscular diaphragm. The diaphragm and ascending duodenum are joined by the suspensory muscle. This muscle’s attachment to the duodenojejunal flexure provides a broader angle for the easier flow of digesting materials, which is thought to aid the digestive system. Moreover, the diaphragm connects to and anchors the liver at its exposed location. A hole in the diaphragm at the level of T10 allows the esophagus to enter the abdomen.
The digestive system is made up of many organs and organ systems that cooperate to ensure the normal intake, digestion, breakdown, absorption, and assimilation of food, as well as the expulsion of waste and waste products from the body. In addition, it is crucial to maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating well, consuming a good diet, and drinking enough water each day in order to keep the digestive system in normal working order.
Planning a trip to Paris ? Get ready !
These are Amazon’s best-selling travel products that you may need for coming to Paris.
Bookstore
- The best travel book : Rick Steves – Paris 2023 – Learn more here
- Fodor’s Paris 2024 – Learn more here
Travel Gear
- Venture Pal Lightweight Backpack – Learn more here
- Samsonite Winfield 2 28″ Luggage – Learn more here
- Swig Savvy’s Stainless Steel Insulated Water Bottle – Learn more here
Check Amazon’s best-seller list for the most popular travel accessories. We sometimes read this list just to find out what new travel products people are buying.